No matter how experienced an investor you are, the decision of when to invest money can naturally provoke a feeling of uncertainty or apprehension.
Are shares too expensive at the moment?
Will rising interest rates cause another sharemarket crash soon?
Am I better off just leaving my money in the bank until a better buying opportunity arises?
These nagging questions can undermine confidence and cause even experienced investors to second guess their investment decisions.
But perhaps the better question is, to what benefit?
In this article, we analyse the experience and fortunes of five hypothetical investors who employ five very simplistic investment strategies over the course of 22 years (Jan 2001 – Dec 2022).
The analysis replicates a study performed by Charles Schwab on the US sharemarket; however, in this example, we focus on how these strategies play out in the Australian market. Each investor received $2,000 at the beginning of every year and invested it as follows:
- Lucky Leo had a knack for timing the market perfectly. Whether through incredible skill or plain luck, he was able to invest his $2,000 at the sharemarket’s lowest level every single year (a feat that even professional or most experienced investors fail to achieve). For example, in 2001, instead of investing his money immediately in January, he waited and invested it on 24 September, which was the Australian sharemarket’s lowest closing level for that year.
- Rapid Riley was far too busy to pay attention to sharemarket news or worry about market timing strategies. She invested her $2,000 on the very first day she could, being the first trading day of the year.
- Steady Eddy appreciated the benefit of long-term sharemarket returns but was also concerned about investing all his money at once, in case of a subsequent market collapse. He employed a dollar cost averaging (DCA) strategy and divided his annual $2,000 into 12 equal investments, which he made at the start of every month.
- Hopeless Harry (like Lucky Leo) attempted to time his investment into the sharemarket at its lowest level each year. However, unlike Leo, Harry had incredibly bad timing and instead managed to time his investment at each year’s market’s peak. For example, in 2001, Harry invested his $2,000 on 29 June, which coincided with the Australian sharemarket’s highest level for that year. He continued to invest at market peaks each year through to 2022.
- Hesitant Hayley was always too nervous to invest her money and would typically have an excuse for “why today was not an opportune time to invest”. Hayley, therefore, left her money sitting in her bank account, which would only earn the interest rate that her bank was offering.
And the winner is …
The chart below displays the accumulated value of each investment strategy as at the end of 2022.
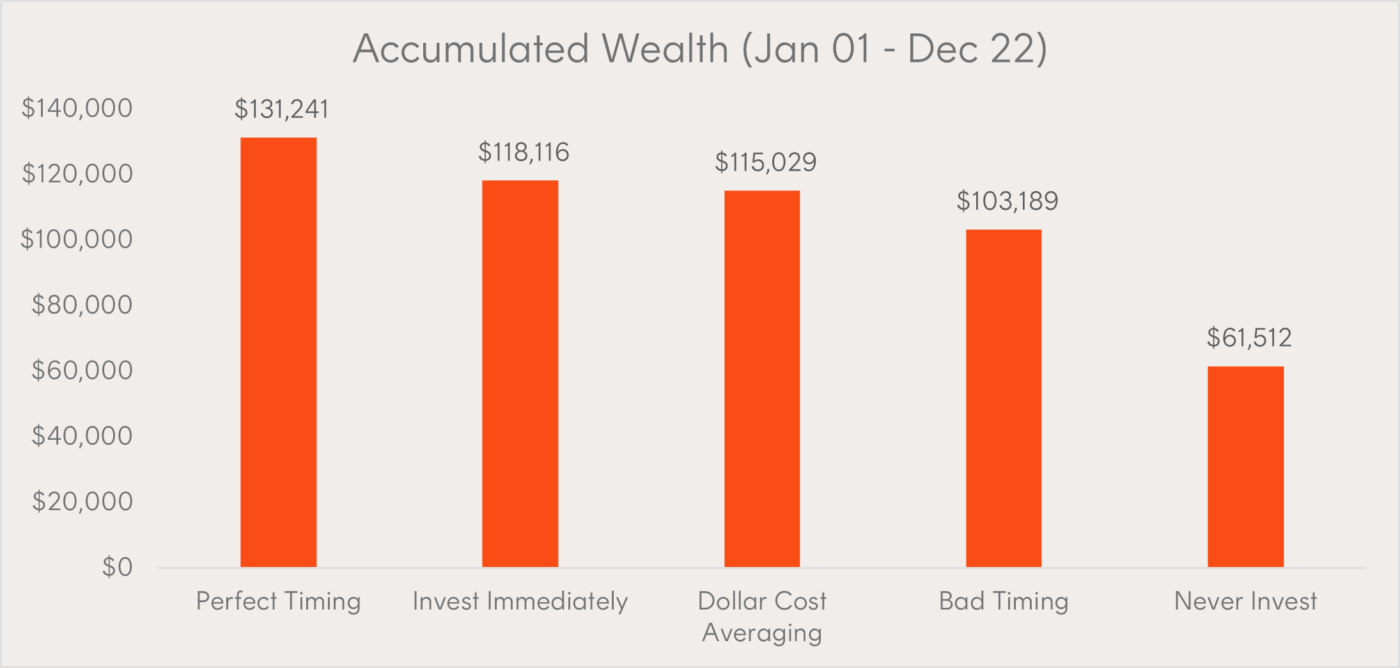
For illustrative purposes only. Individuals invested $2,000 each year into a hypothetical portfolio that tracks the ASX All Ordinaries (INDEXASX: XAO) Accumulation Index. The individual who never invested received a return in line with Bloomberg Ausbond Bank Bill Index
Unsurprisingly, Leo’s strategy of timing the market perfectly every year allowed him to earn first place, as unrealistic as it may be.
However, what was surprising was his somewhat slender winning margin of just $13,125 ahead of Riley, who had simply invested as soon as she could, without any consideration of market timing.
The dollar cost averaging (DCA) strategy employed by Eddy gave him third place and $3,087 less than Riley. A result that can partly be explained by the tendency for sharemarkets to trend upwards over the long-term. This means Eddy, who opted not to invest all his money at the start of the period, would more likely be hurt by ‘up periods’ in the sharemarket, than benefit from ‘down periods’ as he carried out his strategy.
Although Harry’s poor market timing strategy left him $14,927 short of Riley, who had no interest in timing markets, he still accumulated significantly more wealth than had he not invested at all.
Unfortunately for Hayley, she would have been far better off investing at sharemarket peaks – which ironically, was what she was afraid of.
Results stand the test of time
To ensure our findings were no fluke, we examined 24 separate 20-year periods dating back to 1980 (such as 1980-1999, 1981-2000, and so on).
Remarkably, throughout all 24 periods the rankings remained unchanged. The perfect timing strategy provided the highest returns, investing immediately always produced better returns than dollar cost averaging, and bad timing always produced better returns than not investing at all.
Even expanding our analysis to include all possible 30- and 40-year time periods since 1980, we observed the same pattern persisting across all time frames.
Key lessons
- The cost of waiting to invest is high – make a plan and be decisive. While it’s nearly impossible to identify market bottoms accurately and consistently over time, the findings in this study suggest that the benefits of market timing may not be worth the effort or attention in any case. Investors can, in fact, be better served with a considered and structured investment plan that they stick to, regardless of whether the sharemarket is high or low.
- Dollar cost averaging (DCA) overcomes a psychological hurdle – but it also gives up returns. While investing immediately has proven a superior strategy financially, DCA may still be an appropriate strategy for an investor who is anxious about investing all their cash in one go, or who is prone to regret when the market falls suddenly following an investment. DCA, like the ‘invest immediately’ strategy, also eliminates the temptation of market timing and discourages procrastination.
- Over a long time-period, bad market timing still beats not investing at all. Hayley demonstrates the pitfalls from sitting on the sidelines and waiting for the perfect time to invest. From Jan 2001 – Dec 2022 she sacrificed a staggering $41,676 relative to Harry, who continually invested in the sharemarket at the worst possible time. If nothing else, this study has illustrated and reinforced that it’s time in the market, not timing the market, that is key to a successful investment strategy.
While some investors may strive to be the next Lucky Leo of this world, a strategy of perfectly timing the market is completely unrealistic.
In fact, Dow Jones Industrial Average (INDEXDJX: .DJI) 2022 SPIVA data, shows that half of all professional stockpickers underperformed the S&P/ASX 200 (INDEXASX: XJO) benchmark over one year, let alone have a perfect run with their investments.
However, as we’ve learned, with a disciplined investment strategy and adequate investment horizon, positive investment outcomes can still be achieved without the stress of attempting to time markets.


